Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
Tags
- aws
- amazonqcli
- rds
- SageMaker
- serverless
- IaC
- 병목
- terraform
- kubernetes
- 분산시스템
- PACELC
- Validation
- cloudwatch
- CHECK
- CAP
- fcm
- lambda
- Lamda
- sns
Archives
- Today
- Total
잡다한 IT 지식
백준 - 카드 뽑기 본문
본 알고리즘 풀이는 Routine Study에서 진행하고 있습니다.
저를 포함한 구성원이 대부분 초보이므로, 원하시는분은 언제라도 들어오셔도 좋습니다.
문의는 댓글 바람.
문제 출처 : https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/status/16204/1002/1
[문제 설명]
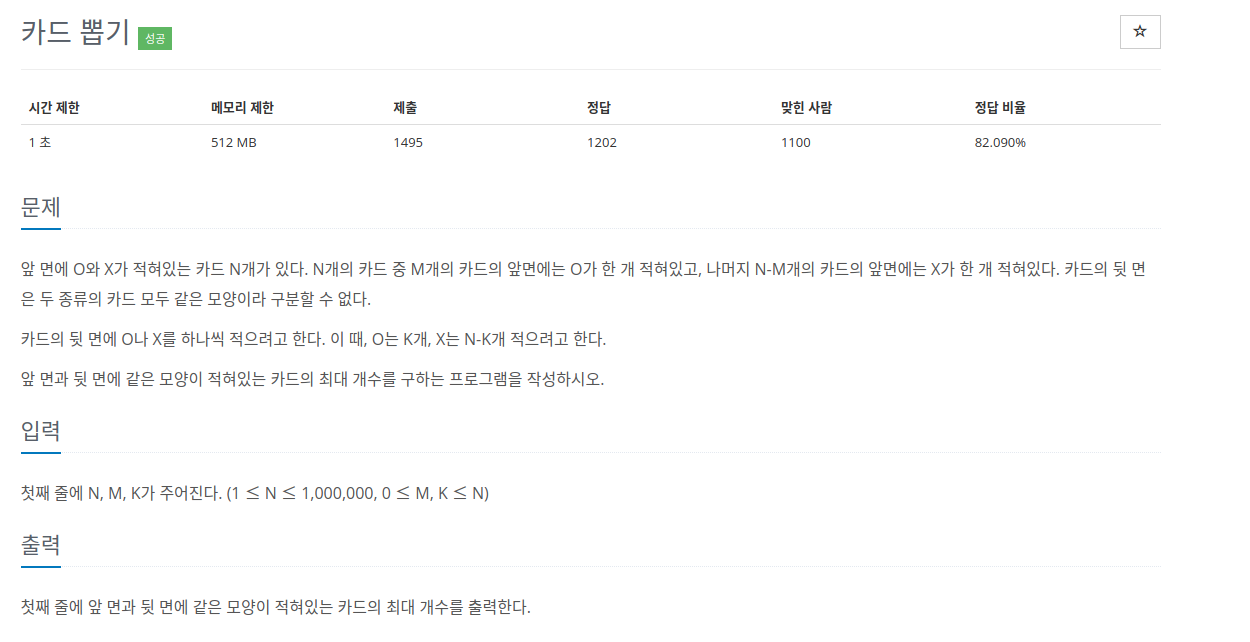
[접근 방법]
M==K이면 양면이 O인 경우 + 양면이 X인 경우 => M + (N-M) => N이 최댓값
M > K이면 K + (N-M)
M < K이면 M + (N-K)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
static int N;
static int M;
static int K;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] inputs = br.readLine().split(" ");
// 전체 개수
N = Integer.parseInt(inputs[0]);
// 앞면이 O인 카드
M = Integer.parseInt(inputs[1]);
// 뒷면이 X인 카드
K = Integer.parseInt(inputs[2]);
// 양면이 O인 카드
int numOfBothCircleCard = Math.min(M,K);
// 양면이 X인 카드
int numOfBothCrossCard = Math.max(M,K);
// 양면이 같은 카드
System.out.println(numOfBothCircleCard + (N-numOfBothCrossCard));
}
}[내 답안 수정하기]
양면이 O인 경우는 무조건 M과 K중에 최솟값이다.
M > K이면 양면이 X인 경우는 N-M이고, M < K이면 양면이 X인 경우는 N-K이다.
M > K인 경우
M과 K는 둘다 양수라는 조건이 있으므로 N-M < N-K이다.
M < K인 경우
마찬가지로 N-K < N-M이다.
즉, M과 K중에서 작은 수가 무조건 O의 최대 개수이고, N-K와 N-M 중 작은 수가 X의 개수가 된다.
[수정 코드]
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
static int N;
static int M;
static int K;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] inputs = br.readLine().split(" ");
// 전체 개수
N = Integer.parseInt(inputs[0]);
// 앞면이 O인 카드
M = Integer.parseInt(inputs[1]);
// 뒷면이 X인 카드
K = Integer.parseInt(inputs[2]);
// 양면이 O인 카드
int numOfBothCircleCard = Math.min(M,K);
// 양면이 X인 카드
int numOfBothCrossCard = Math.min(N-M,N-K);
// 양면이 같은 카드
System.out.println(numOfBothCircleCard + numOfBothCrossCard);
}
}[답지를 참고한 코드]
다른 사람들 답을 보니 StringTokenizer를 사용하면 굉장히 간단하게 입력을 받을 수 있었다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int N;
static int M;
static int K;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," ");
// 전체 개수
int N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// 앞면이 O인 카드
int M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// 뒷면이 X인 카드
int K = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// 양면이 O인 카드
int numOfBothCircleCard = Math.min(M,K);
// 양면이 X인 카드
int numOfBothCrossCard = Math.min(N-M,N-K);
// 양면이 같은 카드
System.out.println(numOfBothCircleCard + numOfBothCrossCard);
}
}
'알고리즘 문제 풀이 > 구현' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 - 기상캐스터 (0) | 2022.01.30 |
|---|---|
| 백준 - 경비원 (0) | 2022.01.17 |
| 백준 - 수강신청 (0) | 2022.01.09 |
| 백준 - 송이의 카드 게임 (0) | 2021.12.30 |
| 백준 - 와글와글 숭고한 (0) | 2021.12.28 |




